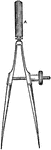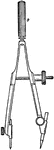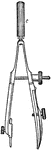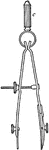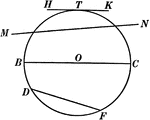
Chords, Secants, Diameters, and Tangents of a Circle
Illustration of a circle with diameter BC, chord DF, secant MN, and tangent HK.
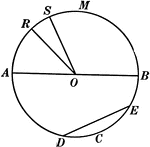
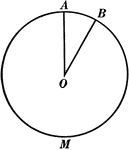
Chords, Diameters, and Radii of a Circle
Illustration of a circle with diameter AB. Radii are RO, SO, AO, and BO. ED is a chord.

Pocket Watch
This pocket watch has a unique design on its back of leaves and circles. The circular handle at the…
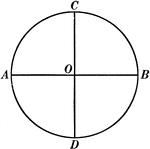
Circle With 2 Perpendicular Diameters
Illustration of a circle with center O and diameters AB and CD perpendicular to each other.
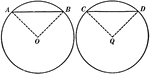
Equal Chords in Equal Circles Theorem
Illustration used to show that "In equal circles, or in the same circle, if two chords are equal, they…
Unequal Chords in Circles Theorem
Illustration used to show that "In equal circles, or in the same circle, if two chords are unequal,…
Equal Chords in Equal Circles Theorem
Illustration used to show that "In equal circles, or in the same circle, if two chords are equal, they…
Unequal Chords in Equal Circles Theorem
Illustration used to show that "In equal circles, or in the same circle, if two chords are unequal,…
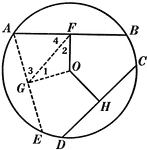
Unequal Chords in Equal Circles Theorem
Illustration used to show that "In equal circles, or in the same circle, if two chords are unequal,…
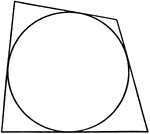
Quadrilateral Circumscribed About a Circle
Illustration of a quadrilateral circumscribed about a circle. This could also be described as a circle…
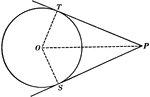
Equal Tangents to Circle Theorem
Illustration used to show that "If two tangents are drawn from any given point to a circle, those tangents…
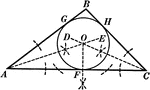
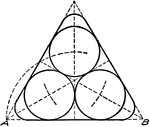
Construction Used to Inscribe a Circle in a Triangle
Illustration used to inscribe a circle in a given triangle.
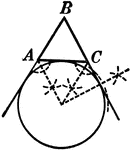
Construction Used to Escribe a Circle to a Triangle
Illustration used to escribe a circle to a given triangle. "A circle which is tangent to one side of…
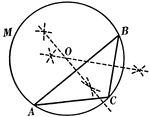
Construction Used to Circumscribe a Circle About a Triangle
Illustration used to circumscribe a circle about a given triangle.
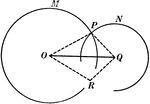
Circumferences of 2 Circles
Illustration used to prove "If two circumferences meet at a point which is not on their line of centers,…
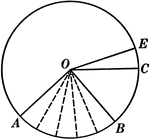
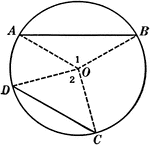
Central Angles and Arcs in a Circle
Illustration of a circle that can be used to show that an "angle at the center of a circle is measured…
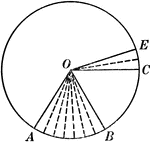
Central Angles and Arcs in a Circle
Illustration of a circle that can be used to show that an "angle at the center of a circle is measured…
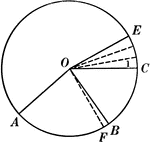
Central Angles and Arcs in a Circle
Illustration of a circle that can be used to show that an "angle at the center of a circle is measured…
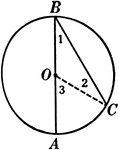
Inscribed Angle in a Circle Proof
Illustration of a circle with an inscribed angle that can be used to prove that "An inscribed angle…
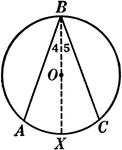
Inscribed Angle in a Circle Proof
Illustration of a circle with an inscribed angle that can be used to prove that "An inscribed angle…
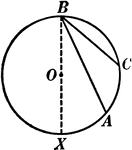
Inscribed Angle in a Circle Proof
Illustration of a circle with an inscribed angle that can be used to prove that "An inscribed angle…
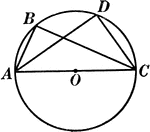
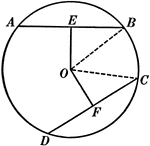
Angles Inscribed in the Same Segment Circle Proof
Illustration of a circle used to prove "All angles inscribed in the same segment are equal."
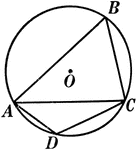
Right Angles Inscribed in Semicircle Proof
Illustration of a circle used to prove "Any angle inscribed in a semicircle is a right angle."
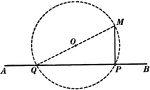
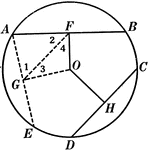
Obtuse Angles Inscribed in Circle Proof
Illustration of a circle used to prove "Any angle inscribed in a segment less than a semicircle is an…
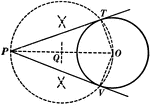
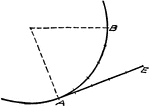
Construction of a Tangent to a Circle
Illustration used to show how "to construct a tangent to a circle from a point outside."
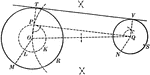
Construction of an External Tangent to 2 Circles
Illustration used to show how "to construct a common external tangent to two given circles."
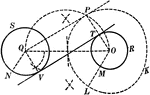
Construction of an 2 External Tangents to 2 Circles
Illustration used to show how to construct two common external tangents to two given circles.

Byzantine Capital
"Byzantine Capital. The leading forms of the Byzantine style are the round arch, the circle, and in…
The Segmentation of the Vitellus
"The first change in the parent-cell is that by which it becomes broken up into a mass of cells, each…
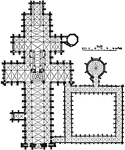
Plan of Salisbury Cathedral, 1075–1092
This is a plan of the Salisbury Cathedral, England. It is an example of English Gothic architecture.…
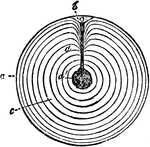
Fowl Ovum
"Meroblastic ovum (yelk) of domestic fowl, bat. size, in section; after haeckel. a, the thin yelk-skin,…
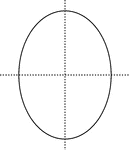
Lines of Symmetry, Oval With
Oval with dotted vertical and horizontal lines that are lines of symmetry.
Center Screw Bow
A center screw bow to draw circles. The adjustable screw is in the middle of the bow.
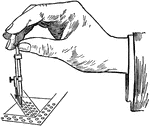
Drop Pen
Drop pen, or rivet pen, can make small circles faster than the bow pen. The pen is useful in bridge…
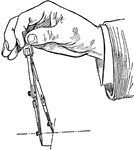
Drawing a Circle Using Compass
When drawing the circle, the compass is turned by the handle with the thumb and forefinger in a clockwise…
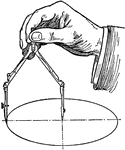
Drawing Large Circles with Compass
"Circles up to perhaps three inches in diameter may be drawn with the legs straight but for larger sizes…
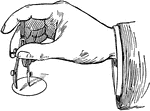
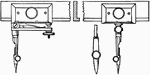
Drawing Small Circles with Bow Instrument
Bow instruments can be used for drawing small circles. Hold the the left hand and spin the nut in or…
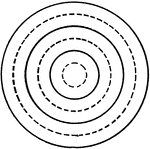
Drawing Concentric Circles with Compass
"Draw Horizontal line throuch center of space. On it mark off radii for six concentric circles 1/4"…
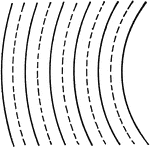
Drawing Concentric Arcs with Compass
"On horizontal center line mark off eleven points 1/4" apart, beginning at left side of space. Draw…
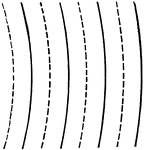
Drawing Concentric Arcs with Compass and Lengthening Bar
"On horizontal center line mark off eight points 3/8" apart, beginning at right side of space." —French,…
Drawing Tangent Circles and Lines with Compass and Triangles
"On base AB, 3 1/2" long construct an equilateral triangle, using the 60-degree triangle. Bisect the…
Rectifying Arc Using Dividers
"In ordinary work the usual way of rectifying an arc is to step around it with the dividers, in spaces…
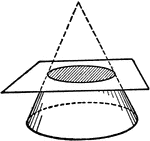
Conic Section Using Circle
The cone is sliced by a circle in a plane perpendicular to the axis. This can be drawn without knowledge…
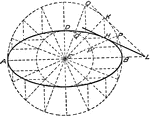
Determining Points on Ellipse Using Circles
Using C as a center, draw two circles with different diameters. The intersection of the diameter lines…
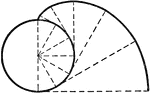
Involute of Circle
"A circle may be conceived as a polygon of an infinite number of sides. Thus to draw the involute of…
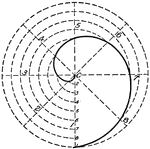
Draw Spiral of Archimedes
"Divide the circumference into a number of equal parts, drawing the radii and numbering the points.…
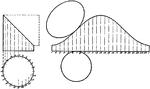
Development of Cylinder
The illustration shows the cylinder rolled out in a tangent plane of the base to create a development…
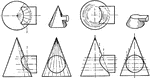
Intersection of Cylinder and Cone
An illustration of finding an intersection of a cone and cylinder by either cutting the vertex of the…
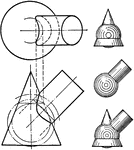
Intersection of Cylinder and Cone
An illustration of finding an intersection of a cone and cylinder by either cutting the vertex of the…